|
Drawing a repetitive graphic from a common starting location
(or an incremented starting location) often creates an
interesting three dimensional looking shape. Take a
look at the following figures and their codes:
import java.awt.*;
import BreezyGUI.*;
public class Demo1 extends GBFrame
{
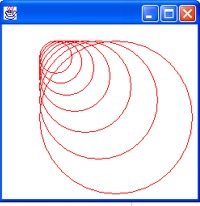
public void paint(Graphics g)
{
int x = 50, y = 50, width
= 40, height = 40;
g.setColor(Color.red);
for (int i = 1; i <=
7; i++)
{
g.drawOval(x, y, height, width);
width =
(int) (width*1.3);
height
= (int) (height*1.3);
}
}
public static void main (String[] args)
{
Frame frm = new
Demo1();
frm.setSize
(250,250);
frm.setVisible(true);
}
}
 |
import java.awt.*;
import BreezyGUI.*;
public class Demo2 extends GBFrame
{
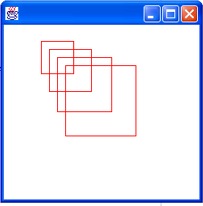
public void paint(Graphics g)
{
int x = 50, y = 50, width
= 40, height = 40;
g.setColor(Color.red);
for (int i = 1; i <= 4; i++)
{
g.drawRect(x, y, height, width);
x = x + 10; y = y + 10;
width =
(int) (width*1.3);
height
= (int) (height*1.3);
}
}
public static void main (String[] args)
{
Frame frm = new
Demo2();
frm.setSize
(250,250);
frm.setVisible(true);
}
}
|
import java.awt.*;
import BreezyGUI.*;
public class Demo3 extends GBFrame
{
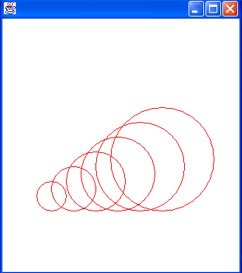
public void paint(Graphics g)
{
int x = 150, y = 150, width
= 140, height = 140;
g.setColor(Color.red);
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++)
{
g.drawOval(x, y, height, width);
x = x -
20; y = y + 20;
width =
(int) (width - 20);
height
= (int) (height - 20);
}
}
public static void main (String[] args)
{
Frame frm = new
Demo3();
frm.setSize
(250,250);
frm.setVisible(true);
}
}
|
import java.awt.*;
import BreezyGUI.*;
public class Demo4 extends GBFrame
{
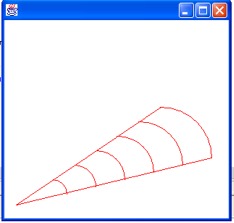
public void paint(Graphics g)
{
int x = 150, y = 150, width
= 140, height = 140;
g.setColor(Color.red);
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++)
{
g.drawArc(x, y, height, width, 0, 90);
x = x -
20; y = y + 20;
width =
(int) (width - 20);
height
= (int) (height - 20);
}
g.drawLine(220,150, 20,285);
g.drawLine(290,220, 20,285);
}
public static void main (String[] args)
{
Frame frm = new
Demo4();
frm.setSize
(250,250);
frm.setVisible(true);
}
}
|
|